Table of Contents Show
Power distribution companies (DISCOMs) in India are reeling under mounting financial stress. The recent pandemic clearly demonstrated how vulnerable this precarious financial condition is – as DISCOM debts promptly rose back to pre-UDAY levels in a matter of months. This shows that the status quo is not sustainable and changing times demand an agile and dynamic strategy. This must be suitably aided with technological innovation that cuts across processes of the entire value chain. More so because of rising expectations of customers who are more aware, more connected and more vocal than ever before. Add to this the looming threat of competition. Thus, in the post-covid era, digital transformation in DISCOMs is no longer an option – it is imperative.
Change is the only constant in life.
Heraclitus, Greek philosopher, 535 B.C.
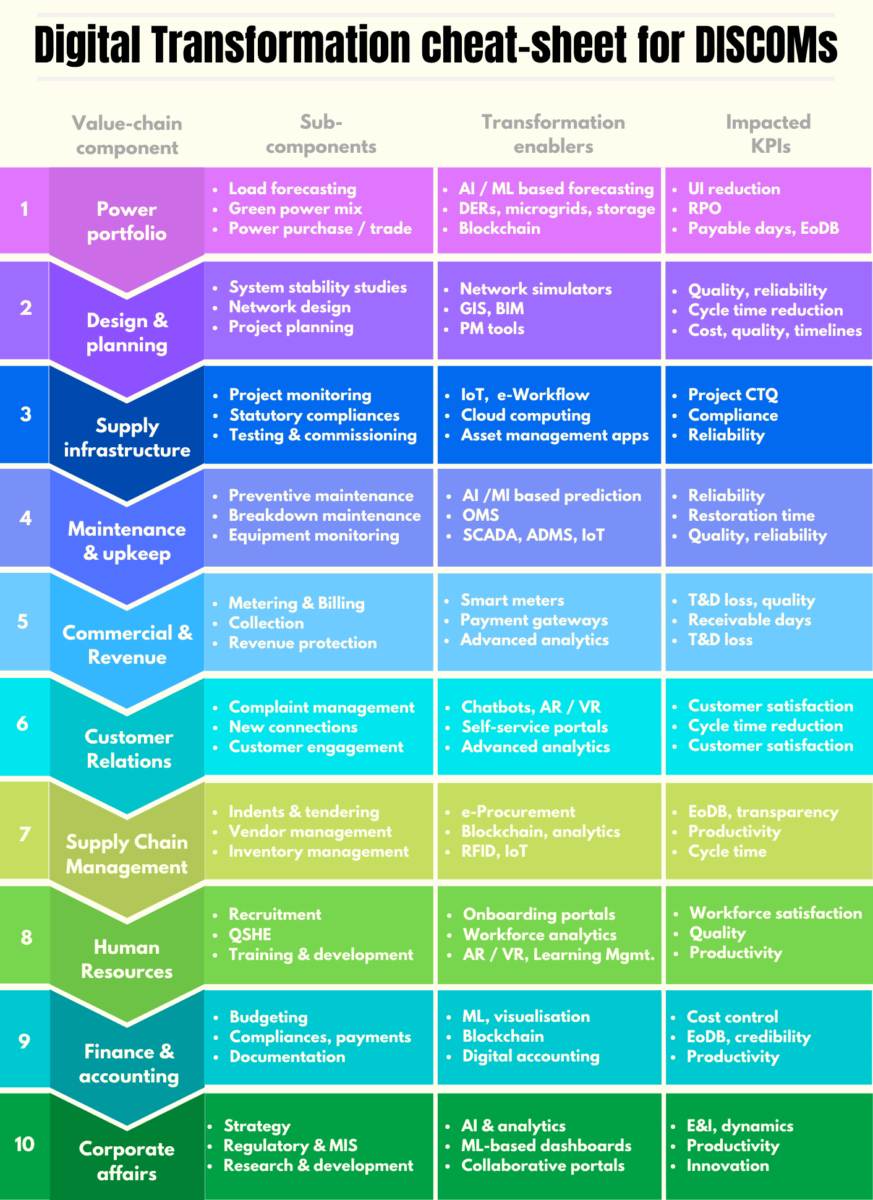
As we classify key components of the DISCOM’s value chain into primary and support functions, it is interesting to map out the technology platforms appropriate for important sub-components within each function. Further, the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that would get impacted by technological interventions can also be mapped. This exercise can help to find opportunities for integration to leverage the full potential of digital transformation in DISCOMs. A cheat-sheet is provided at the end that can be used for this purpose.
Download the pdf version here – Cheat-sheet for Digital transformation in DISCOMs
The ten main value chain components (including support functions) are as follows –
Power portfolio
Power portfolio management has a separate function in most progressive DISCOMs. In some states, it is centrally controlled for multiple DISCOMs in that state. Private DISCOMs usually have a dedicated power purchase and trading desk for greater focus on their input cost.
DISCOMs can leverage digital transformation in power portfolio management by implementing advanced technologies such as blockchain, AI / ML and automated microgrids. For instance, UP Power Corporation Ltd. (UPPCL) implemented a blockchain-based mechanism for solar power trading. Using blockchain technology for power trading can increase transparency, reduce transaction costs, and improve the efficiency of the power trading process. Top candidates for potential technology infusion are given in the table below –
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Load forecasting | AI / ML based forecasting | Reduction in Unscheduled Interchange (UI) charges |
| Green power mix | DERs, microgrids, etc. | Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) |
| Power purchase / trade | Blockchain | Payable days, Ease of Doing Business (EoDB) |
Design and planning
Technical design and planning is usually carried out by the project or technical department. Names might vary from state to state. Essentially they have the same function. Here, I took a different set of Technology tools are applicable. For instance, by using Geographical Information System (GIS), DISCOMs can create digital maps of their distribution network that integrate various data such as customer locations, transformer locations, and distribution lines. This enables them to visualize and analyze the distribution network in a much more comprehensive and accurate manner. This can help in identifying areas of congestion, inefficiency, and potential for expansion.
Gegraphical Information Systems (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) can be used to create a digital twin of the distribution network. These can be used in tandem with network analysis tools to simulate different scenarios, such as the impact of adding new substations or distribution lines, or the effect of upgrading existing infrastructure. This can help DISCOMs in identifying areas of inefficiency and potential for improvement, and in making more informed decisions about network expansion and upgrade. Top candidates for technology infusion in design and planning are given in the table below –
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| System stability studies | Network simulators | Quality, reliability |
| Network design | GIS, BIM | Cycle time reduction |
| Project planning | PM tools | Cost, quality, timelines |
Supply infrastructure
IoT-enabled devices can be used to improve the accuracy of data collection and monitoring of the distribution network during the construction process, which can help in identifying and rectifying issues quickly. This can also enable automation of the construction process and improve project cost, quality and timeliness metrics.
Cloud computing can be used to store and manage large amounts of data generated during the EPC process, such as project schedules, financial data, and engineering drawings. This can enable real-time collaboration and communication among different stakeholders, such as contractors, engineers, and project managers. This can not only improve the efficiency and speed of the EPC process, but also help DISCOMs improve the degree of compliance to schedules, statutory and legal requirements.
Top areas for technology deployment are as follows –
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Project monitoring | IoT, e-Workflow | Project CTQ |
| Statutory compliances | Cloud computing | Efficiency, Degree of compliance |
| Testing & commissioning | Asset management apps | Reliability |
Maintenance and upkeep
Asset management software can be used to track and manage the lifecycle of distribution network assets, such as transformers, switchgear, and power lines. Predictive analytics on the data collected from OMS, IoT devices, etc. can help DISCOMs to determine when equipment are likely to fail and schedule maintenance accordingly. This can enable DISCOMs to schedule maintenance and replacement of assets based on their working condition, rather than on a fixed schedule. Additionally, it can provide a centralized access control for all maintenance and repair data, which can be used to improve the maintenance planning process. It may be noted that lack of structured maintenance and repair data is one of the main challenges in DISCOM operations.
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Preventive maintenance | AI /Ml based prediction | Reliability |
| Breakdown maintenance | Outage Management Systems (OMS) | Restoration time |
| Equipment monitoring | SCADA, ADMS, IoT | Quality, reliability |
Commercial and revenue
DISCOMs can gain real-time visibility into energy consumption patterns and identify areas of inefficiency by leveraging Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and associated ML-based analytics layer. This can help them to improve efficiency of energy distribution and reduce losses.
Read more about how DISCOMs can improve the implementation of smart metering schemes here
Overall, digital transformation in Metering, Billing and Collection (MBC) can help DISCOMs to improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer engagement. All of these factors largely contribute to increased revenues – propelling DISCOMs towards financial viability.
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Metering & Billing | Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) | T&D loss, quality |
| Collection | Payment gateways | Receivable days |
| Revenue protection | Advanced analytics, ML | T&D loss |
Customer relations
DISCOMs can develop interactive online portals with chatbots, AR / VR integration, etc. These would enable customers to view their consumption data, pay bills, and request special, customized services. Technology enablers in customer relationship management can improve engagement and reduce the workload of DISCOM staff by reducing physical footfall. Top sub-components, technology enablers and benefits of digital transformation in DISCOMs’ CRM activities are as follows –
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Complaint management | Chatbots, AR / VR | Customer satisfaction |
| New connections | Self-service portals | Cycle time reduction |
| Customer engagement | Advanced analytics | Customer satisfaction |
Supply chain management
DISCOMs leverage digital tools such as RFID and IoT sensors to gain real-time visibility into the location and condition of goods as they move through the supply chain. Predictive analytics can provide insights into future demand to enable DISCOMs to plan their supply chain accordingly.
Blockchain can be used to create tamper-proof records of all transactions in the supply chain, increasing transparency and trust among all parties involved. This will in-turn help to bridge the widening trust-deficit that DISCOMs have with vendors. Here are some typical use cases for technology enablement in SCM –
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Indents & tendering | e-Procurement | EoDB, transparency |
| Vendor management | Blockchain, analytics | Productivity |
| Inventory management | RFID, IoT | Cycle time |
Human resources
DISCOMs can provide employees with access to Learning Management Systems (LMS) for training and development opportunities and track their progress. This can be further complemented with suitable AR / VR platforms which can help employees to grasp learning concepts more effectively without the need for centralised training infrastructure.
Read more on metaverse use cases in utilities
The following solutions can enable DISCOMs to improve productivity, enhance employee engagement, and increase the effectiveness of their human resource management.
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Recruitment | Onboarding portals | Workforce satisfaction |
| QSHE | Workforce analytics | Quality |
| Training & development | AR / VR, Learning Mgmt. | Productivity |
Finance and accounting
ML-based prediction, advanced data visualization, blockchain and digital accounting are some of the go-to technology enablers for the DISCOM finance and accounts function. Armed with the right set of technology tools, F&A can improve credibility (credit ratings), ease of doing business index, productivity, etc. while keeping their costs under control so as to pass on only prudent cost to customers as the regulatory environment demands. Sub-component-wise benefits are shown in the table below –
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Budgeting | ML, visualisation | Cost control |
| Compliances, payments | Blockchain | EoDB, credibility |
| Documentation | Digital accounting | Productivity |
Corporate affairs
AI / ML based dashboards deploying advanced analytics can be used to provide a custom view of actionable information from large amounts of data. This data may be sourced from various digital inputs, such as smart meter data, weather data, and customer data. This can help the governance structure in DISCOMs to gain insights into customer behaviour, predict future demand, and identify important patterns and trends for better decision making. For example, MDs of DISCOMs may want to focus on divisional teams with tougher performance challenges and risks. Superintending Engineers can monitor performance of teams at a granular section or sub-divisional level. While sectional team leaders (such as JEs / AEs) can target specific incentive schemes to promote good performance at individual levels.
| Sub-component | Technology enablers | Benefits / impacted KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy | AI & analytics | Strategy evaluation & improvement (E&I) |
| Regulatory & MIS | ML-based dashboards | Productivity |
| Research & development | Collaborative portals | Innovation |
Conclusion
As seen in the sections above, there is potential for leveraging digital transformation in DISCOMs across the value-chain components and sub-components. However, the key is to integrate the transformation enablers in such a way that it serves the overall goal of the DISCOM. For instance, if the OMS layer is seamlessly integrated with GIS, ADMS and SCADA, DISCOMs can provide faster restoration in case of unplanned outages by automated action on redundancy switching. In case of radial networks, they can respond by providing precise information to customers on the breakdown response and expected restoration time. This is just one example out of the hundreds of potential technology integration outcomes.
Therefore, by leveraging these digital transformation, DISCOMs can improve their overall efficiency, reliability and cost-effectiveness and ensure smooth turn-around of their financial situation.
A handy cheat-sheet based on the above-mentioned analysis is given below for the reader’s reference –







good insight for discom utility — future transformation toward digital -as per current scenario requirement…